FENa Calculator: Tool for Kidney Function Assessment
The FENa Calculator is a reliable medical tool for calculating the Fractional Excretion of Sodium (FENa). This calculator helps healthcare professionals differentiate pre-renal from intrinsic renal acute kidney injury with precision and accuracy.
What is FENa Calculator?
The FENa Calculator is an advanced medical calculation tool designed to determine the percentage of filtered sodium excreted in urine. As a specialized medical calculator, it processes both urine and serum measurements of sodium and creatinine to provide crucial insights into kidney function. Healthcare professionals worldwide trust the FENa Calculator to assist in their clinical decision-making process when evaluating acute kidney injury (AKI).
Our FENa Calculator stands out for its accuracy and ease of use, making it an indispensable tool in both emergency and routine clinical settings. Whether you're a nephrologist, emergency physician, or general practitioner, this FENa Calculator provides quick and reliable results to support your diagnostic process.
Benefits of Using Our FENa Calculator
The FENa Calculator offers numerous advantages in clinical practice:
- Instant and accurate calculations that eliminate manual computation errors
- User-friendly interface designed for quick data entry during busy clinical shifts
- Clear result interpretation guidelines to support clinical decision-making
- Mobile-optimized design allowing access to the FENa Calculator anywhere, anytime
- Regular updates to ensure alignment with current medical guidelines
Healthcare professionals choose our FENa Calculator for its reliability and clinical relevance in kidney function assessment.
Clinical Applications of FENa Calculator
The FENa Calculator serves multiple clinical purposes:
- Emergency Department: Quick assessment of acute kidney injury etiology
- Nephrology Consultations: Detailed evaluation of kidney function
- Critical Care: Monitoring kidney function in critically ill patients
- Internal Medicine: Differential diagnosis of decreased kidney function
- Research: Standardized assessment of kidney function in clinical studies
Tips for Accurate FENa Calculation
To ensure the most accurate results from your FENa Calculator:
- Collect all samples (urine and blood) within the same timeframe
- Ensure proper specimen handling and laboratory processing
- Document any medications that might affect results, especially diuretics
- Consider the patient's volume status and recent fluid administration
- Review results in context with other clinical and laboratory findings
Remember that the FENa Calculator is most reliable when used as part of a comprehensive clinical assessment.
How to calculate FENa?
The Fractional Excretion of Sodium (FENa) is calculated using the following formula:
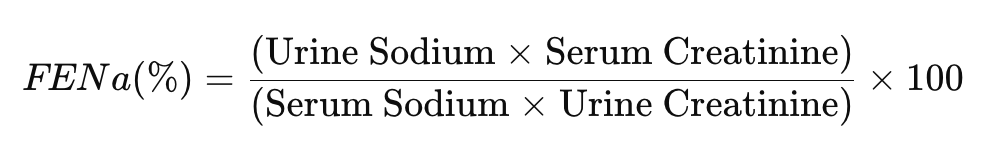
Where:
- Urine Sodium (UNa) and Serum Sodium (SNa) are measured in mEq/L
- Urine Creatinine (UCr) and Serum Creatinine (SCr) are measured in mg/dL
Why use FENa Calculator?
FENa calculation is valuable because it helps differentiate between two major types of acute kidney injury:
- Pre-renal AKI (caused by decreased blood flow to the kidneys)
- Intrinsic renal AKI (caused by damage to the kidney tissue itself)
This distinction is crucial as it guides treatment decisions and helps determine the appropriate therapeutic approach.
When to use FENa Calculator?
- When a patient presents with acute kidney injury
- During the initial evaluation of worsening kidney function
- To help determine if fluid resuscitation might be beneficial
- When distinguishing between pre-renal and intrinsic renal causes of AKI is clinically important
Important Considerations
- All measurements should be taken at the same time or as close as possible
- Results may be unreliable in patients taking diuretics
- Values should be entered in the correct units (mEq/L for sodium, mg/dL for creatinine)
- FENa should be interpreted alongside other clinical findings and not in isolation
- Certain conditions like sepsis can affect the reliability of FENa calculations
Interpreting FENa Results
FENa < 1%
Suggests pre-renal AKI:
- Indicates normal tubular function
- Common in volume depletion or decreased renal perfusion
- Often reversible with fluid resuscitation
FENa > 1%
Suggests intrinsic renal AKI:
- Indicates tubular dysfunction
- Common in acute tubular necrosis
- May require more intensive management
This calculator is for informational purposes only. Always consult with a healthcare provider for medical advice.
References
- Steiner RW. Interpreting the fractional excretion of sodium. Am J Med. 1984;77(4):699-702. doi:10.1016/0002-9343(84)90368-6
- Espinel CH. The FENa test: use in the differential diagnosis of acute renal failure. JAMA. 1976;236(6):579-581. doi:10.1001/jama.1976.03270060029022
- Perazella MA, Coca SG. Traditional urinary biomarkers in the assessment of hospital-acquired AKI. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012;7(1):167-174. doi:10.2215/CJN.09490911
- Bagshaw SM, Langenberg C, Bellomo R. Urinary biochemistry and microscopy in septic acute renal failure: a systematic review. Am J Kidney Dis. 2006;48(5):695-705. doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2006.07.017
- Carvounis CP, Nisar S, Guro-Razuman S. Significance of the fractional excretion of urea in the differential diagnosis of acute renal failure. Kidney Int. 2002;62(6):2223-2229. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1755.2002.00683.x
- Miller TR, Anderson RJ, Linas SL, et al. Urinary diagnostic indices in acute renal failure: a prospective study. Ann Intern Med. 1978;89(1):47-50. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-89-1-47
- Zarich S, Fang LS, Diamond JR. Fractional excretion of sodium: exceptions to its diagnostic value. Arch Intern Med. 1985;145(1):108-112. doi:10.1001/archinte.1985.00360010128020